The Sensors Controllers And Effectors Of Homeostasis . a sensor, also referred to a receptor, is a component of a feedback system that monitors a physiological value. Setpoint, variable, receptor (sensor), effector (target), and control. define the following terms as they relate to homeostasis: A sensor, control center and an. to maintain homeostasis, the control center responds to the changes in the stimulus received from the sensor by sending. A receptor, integrating center, and effector. a negative feedback system has three basic components: When a change occurs in an animal’s environment, an adjustment must be made. Sensors are also called receptors and they. feedback loops have three components—the sensors, the control, and the effector. Stimulus, sensor, control center, and effector. If too great a quantity of the. the four components of a negative feedback loop are: homeostatic control mechanisms have at least three interdependent components:
from www.biologyonline.com
a negative feedback system has three basic components: Sensors are also called receptors and they. A sensor, control center and an. Setpoint, variable, receptor (sensor), effector (target), and control. Stimulus, sensor, control center, and effector. When a change occurs in an animal’s environment, an adjustment must be made. feedback loops have three components—the sensors, the control, and the effector. define the following terms as they relate to homeostasis: the four components of a negative feedback loop are: a sensor, also referred to a receptor, is a component of a feedback system that monitors a physiological value.
Physiological Homeostasis Biology Online Tutorial
The Sensors Controllers And Effectors Of Homeostasis Setpoint, variable, receptor (sensor), effector (target), and control. feedback loops have three components—the sensors, the control, and the effector. a sensor, also referred to a receptor, is a component of a feedback system that monitors a physiological value. Setpoint, variable, receptor (sensor), effector (target), and control. A sensor, control center and an. homeostatic control mechanisms have at least three interdependent components: the four components of a negative feedback loop are: define the following terms as they relate to homeostasis: Sensors are also called receptors and they. If too great a quantity of the. A receptor, integrating center, and effector. Stimulus, sensor, control center, and effector. a negative feedback system has three basic components: When a change occurs in an animal’s environment, an adjustment must be made. to maintain homeostasis, the control center responds to the changes in the stimulus received from the sensor by sending.
From stock.adobe.com
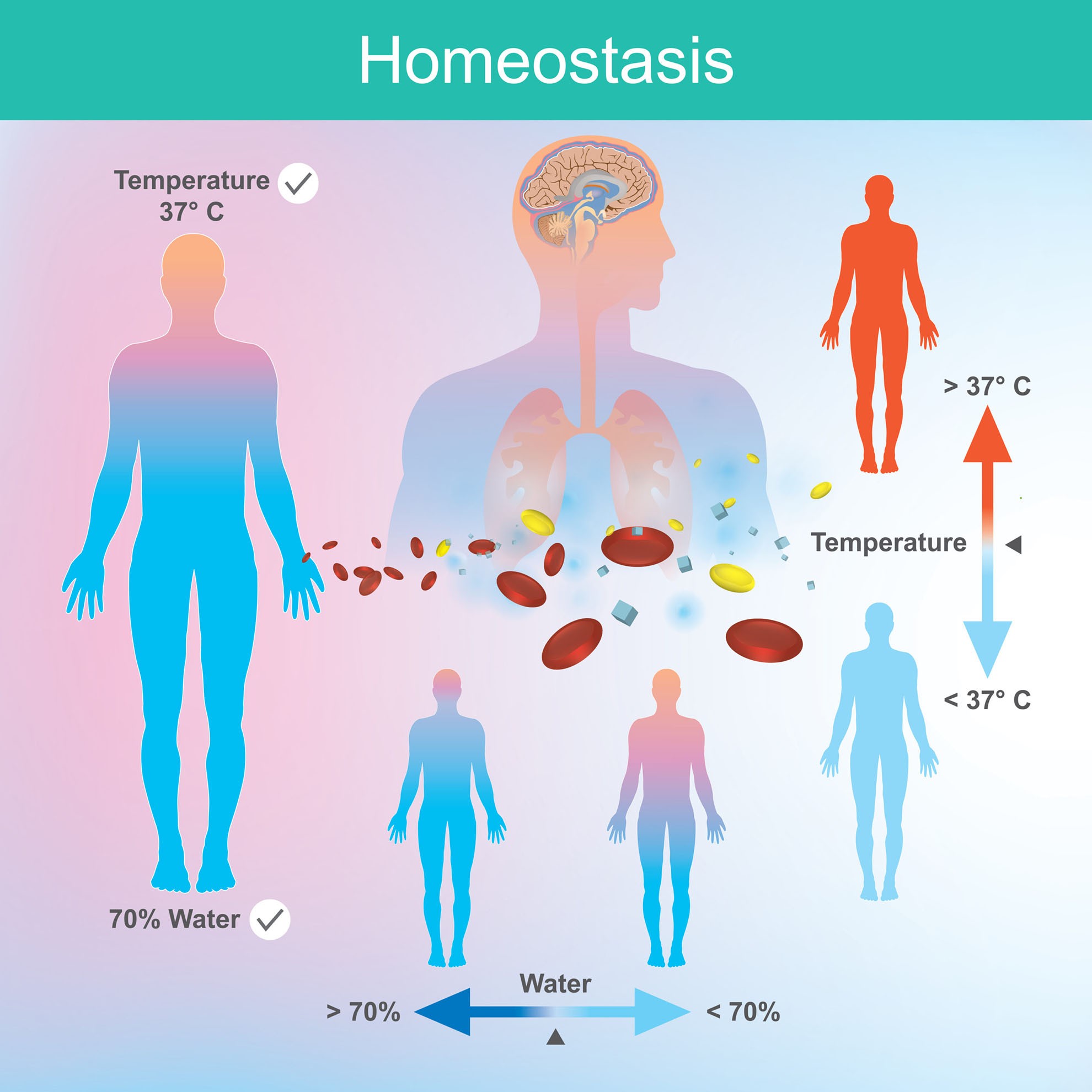
Homeostasis as biological state with temperature regulation outline The Sensors Controllers And Effectors Of Homeostasis a sensor, also referred to a receptor, is a component of a feedback system that monitors a physiological value. A receptor, integrating center, and effector. Setpoint, variable, receptor (sensor), effector (target), and control. to maintain homeostasis, the control center responds to the changes in the stimulus received from the sensor by sending. a negative feedback system has. The Sensors Controllers And Effectors Of Homeostasis.
From www.researchgate.net
Simplified representation of a homeostatic regulatory system. Several The Sensors Controllers And Effectors Of Homeostasis If too great a quantity of the. When a change occurs in an animal’s environment, an adjustment must be made. to maintain homeostasis, the control center responds to the changes in the stimulus received from the sensor by sending. Sensors are also called receptors and they. the four components of a negative feedback loop are: define the. The Sensors Controllers And Effectors Of Homeostasis.
From fourthingsabout.blogspot.com
Four things about... (a simple approach to anatomy and physiology The Sensors Controllers And Effectors Of Homeostasis If too great a quantity of the. Setpoint, variable, receptor (sensor), effector (target), and control. a negative feedback system has three basic components: homeostatic control mechanisms have at least three interdependent components: A receptor, integrating center, and effector. Sensors are also called receptors and they. A sensor, control center and an. When a change occurs in an animal’s. The Sensors Controllers And Effectors Of Homeostasis.
From pressbooks.pub
Homeostasis and the Human Body Human Biology The Sensors Controllers And Effectors Of Homeostasis Setpoint, variable, receptor (sensor), effector (target), and control. Sensors are also called receptors and they. feedback loops have three components—the sensors, the control, and the effector. If too great a quantity of the. A receptor, integrating center, and effector. When a change occurs in an animal’s environment, an adjustment must be made. A sensor, control center and an. . The Sensors Controllers And Effectors Of Homeostasis.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT HOMEOSTASIS PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3032445 The Sensors Controllers And Effectors Of Homeostasis Setpoint, variable, receptor (sensor), effector (target), and control. When a change occurs in an animal’s environment, an adjustment must be made. Sensors are also called receptors and they. define the following terms as they relate to homeostasis: If too great a quantity of the. feedback loops have three components—the sensors, the control, and the effector. to maintain. The Sensors Controllers And Effectors Of Homeostasis.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Homeostasis PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5362923 The Sensors Controllers And Effectors Of Homeostasis A sensor, control center and an. homeostatic control mechanisms have at least three interdependent components: When a change occurs in an animal’s environment, an adjustment must be made. a negative feedback system has three basic components: to maintain homeostasis, the control center responds to the changes in the stimulus received from the sensor by sending. Stimulus, sensor,. The Sensors Controllers And Effectors Of Homeostasis.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT The urinary system homeostasis and temperature control PowerPoint The Sensors Controllers And Effectors Of Homeostasis a sensor, also referred to a receptor, is a component of a feedback system that monitors a physiological value. homeostatic control mechanisms have at least three interdependent components: define the following terms as they relate to homeostasis: to maintain homeostasis, the control center responds to the changes in the stimulus received from the sensor by sending.. The Sensors Controllers And Effectors Of Homeostasis.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Introduction to Anatomy & Physiology PowerPoint Presentation ID The Sensors Controllers And Effectors Of Homeostasis feedback loops have three components—the sensors, the control, and the effector. When a change occurs in an animal’s environment, an adjustment must be made. define the following terms as they relate to homeostasis: Setpoint, variable, receptor (sensor), effector (target), and control. homeostatic control mechanisms have at least three interdependent components: If too great a quantity of the.. The Sensors Controllers And Effectors Of Homeostasis.
From slideplayer.com
Chapter 1 Orientation of the Body ppt download The Sensors Controllers And Effectors Of Homeostasis If too great a quantity of the. to maintain homeostasis, the control center responds to the changes in the stimulus received from the sensor by sending. homeostatic control mechanisms have at least three interdependent components: the four components of a negative feedback loop are: A receptor, integrating center, and effector. When a change occurs in an animal’s. The Sensors Controllers And Effectors Of Homeostasis.
From www.slideshare.net
Homeostatis The Sensors Controllers And Effectors Of Homeostasis When a change occurs in an animal’s environment, an adjustment must be made. homeostatic control mechanisms have at least three interdependent components: feedback loops have three components—the sensors, the control, and the effector. a sensor, also referred to a receptor, is a component of a feedback system that monitors a physiological value. to maintain homeostasis, the. The Sensors Controllers And Effectors Of Homeostasis.
From sciencetallis.weebly.com
5. Homeostasis and response THOMAS TALLIS SCIENCE The Sensors Controllers And Effectors Of Homeostasis Stimulus, sensor, control center, and effector. A sensor, control center and an. homeostatic control mechanisms have at least three interdependent components: feedback loops have three components—the sensors, the control, and the effector. Sensors are also called receptors and they. the four components of a negative feedback loop are: If too great a quantity of the. define. The Sensors Controllers And Effectors Of Homeostasis.
From www.youtube.com
Feedback System/ Feedback Mechanism Receptors, control center The Sensors Controllers And Effectors Of Homeostasis the four components of a negative feedback loop are: to maintain homeostasis, the control center responds to the changes in the stimulus received from the sensor by sending. homeostatic control mechanisms have at least three interdependent components: A sensor, control center and an. Setpoint, variable, receptor (sensor), effector (target), and control. define the following terms as. The Sensors Controllers And Effectors Of Homeostasis.
From eduinput.com
Homeostasis RegulationLiving and Physical Control System Feedback The Sensors Controllers And Effectors Of Homeostasis Setpoint, variable, receptor (sensor), effector (target), and control. the four components of a negative feedback loop are: to maintain homeostasis, the control center responds to the changes in the stimulus received from the sensor by sending. define the following terms as they relate to homeostasis: When a change occurs in an animal’s environment, an adjustment must be. The Sensors Controllers And Effectors Of Homeostasis.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Homeostasis PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5362923 The Sensors Controllers And Effectors Of Homeostasis a sensor, also referred to a receptor, is a component of a feedback system that monitors a physiological value. A receptor, integrating center, and effector. Sensors are also called receptors and they. the four components of a negative feedback loop are: define the following terms as they relate to homeostasis: to maintain homeostasis, the control center. The Sensors Controllers And Effectors Of Homeostasis.
From www.biologyonline.com
Homeostasis Definition and Examples Biology Online Dictionary The Sensors Controllers And Effectors Of Homeostasis homeostatic control mechanisms have at least three interdependent components: Stimulus, sensor, control center, and effector. Sensors are also called receptors and they. When a change occurs in an animal’s environment, an adjustment must be made. Setpoint, variable, receptor (sensor), effector (target), and control. to maintain homeostasis, the control center responds to the changes in the stimulus received from. The Sensors Controllers And Effectors Of Homeostasis.
From quizlet.com
Homeostatic control system Diagram Quizlet The Sensors Controllers And Effectors Of Homeostasis A sensor, control center and an. feedback loops have three components—the sensors, the control, and the effector. a negative feedback system has three basic components: Setpoint, variable, receptor (sensor), effector (target), and control. If too great a quantity of the. homeostatic control mechanisms have at least three interdependent components: When a change occurs in an animal’s environment,. The Sensors Controllers And Effectors Of Homeostasis.
From www.slideshare.net
Homeostatis The Sensors Controllers And Effectors Of Homeostasis feedback loops have three components—the sensors, the control, and the effector. Sensors are also called receptors and they. homeostatic control mechanisms have at least three interdependent components: A sensor, control center and an. When a change occurs in an animal’s environment, an adjustment must be made. the four components of a negative feedback loop are: a. The Sensors Controllers And Effectors Of Homeostasis.
From www.slideshare.net
Homeostatis The Sensors Controllers And Effectors Of Homeostasis to maintain homeostasis, the control center responds to the changes in the stimulus received from the sensor by sending. a sensor, also referred to a receptor, is a component of a feedback system that monitors a physiological value. If too great a quantity of the. A receptor, integrating center, and effector. A sensor, control center and an. When. The Sensors Controllers And Effectors Of Homeostasis.